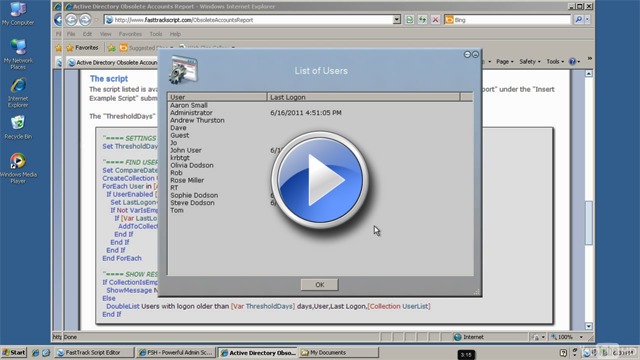
Script output
The example script below will list all user accounts that have not been logged on with within a configurable number of days.
When running the script, the list presented could look like this:
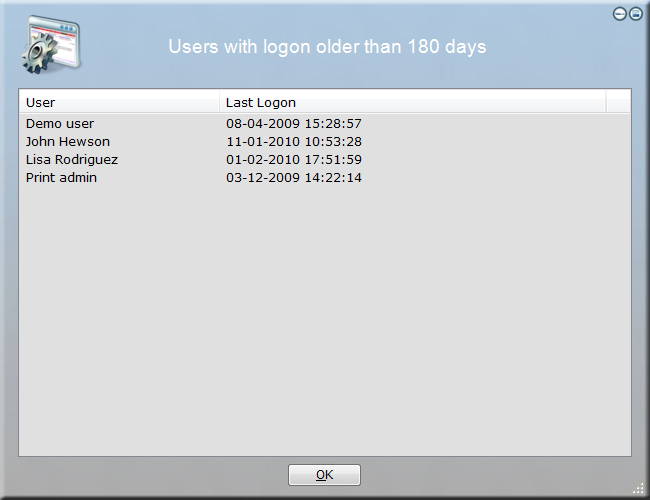
In this example, it is pretty obvious that the "Print admin" account is a temporary account that has
not been used for years. The "Demo user" account also looks suspicious. The others two accounts could
be users that are no longer employed in the company. These will require further investigation to determine,
if these can be deleted or disabled.
The advantage of scripting this instead of purchasing commercial software to do this, is that you can
customize it any way you like and build your own custom versions of it - with little effort. For example:
- You could compile an exe file for the Human Resource department to list all user candidates that might be obsolete.
- With an extra UserIsAdmin condition, you could build a version for yourself that lists only domain admins, who have not logged on for a much shorter period of time.
- You may only want to investigate a subset of users. The example script below looks at all users. To have it
look at users only in a specific Organizational Unit, the
collection AllUsers could simply be replaced by the UsersInOU collection. You could build
additional logic to further filter the users listed, for instance based on other Active
Directory attributes and properties.
- You need a different report. For example using a "Not UserHasPasswordExpiry" condition instead of extracting logon date will show you a list of users that do not have password expiry instead.
The script
The script listed is available directly in the script editor: Go to the "Documentation" tab,
select "Obsolete User Accounts Report" under the "Insert Example Script" submenu. When the script is visible
in the editor, simply press F5 to execute it.
The "ThresholdDays" setting is the threshold in number of days of when accounts are included in the list.
''====
SETTINGS ====
Set ThresholdDays=180
''==== FIND
USERS ====
Set CompareDate=[SubtractDays [Var ThresholdDays]]
CreateCollection UserList
ForEach User in [AllUsers]
If UserEnabled
[Var User] Then
Set LastLogon=[UserLastLogon [Var User]]
If Not VarIsEmpty LastLogon Then
If [Var LastLogon]<[Var CompareDate] Then
AddToCollection
UserList,[Var User],[Var LastLogon]
End If
End If
End If
End ForEach
''==== SHOW
RESULT ====
If CollectionIsEmpty
UserList Then
ShowMessage No active users
have logon older than [Var ThresholdDays] days.
Else
DoubleList Users with logon
older than [Var ThresholdDays] days,User,Last Logon,[Collection UserList]
End If
Modified version to list obsolete computer accounts
The above script can easily be re-written to list obsolete computer accounts instead. All the
same attributes that exist on user accounts also exist on computer accounts. This means that
the script can be modified to list computers instead of users simply by replacing the Active
Directory user functionality with the equivalent functionality for Active Directory computers,
as listed below.
This script is also available directly in the script editor: Go to the "Documentation" tab,
select "Obsolete Computer Accounts Report" under the "Insert Example Script" submenu.
When the script is visible in the editor, simply press F5 to execute it.
''====
SETTINGS ====
Set ThresholdDays=180
''==== FIND
COMPUTERS ====
Set CompareDate=[SubtractDays [Var ThresholdDays]]
CreateCollection ComputerList
ForEach Computer in [AllComputers]
If ComputerEnabled
[Var Computer] Then
Set LastLogon=[ComputerLastLogon [Var Computer]]
If Not VarIsEmpty LastLogon Then
If [Var LastLogon]<[Var CompareDate] Then
AddToCollection
ComputerList,[Var Computer],[Var LastLogon]
End If
End If
End If
End ForEach
''==== SHOW
RESULT ====
If CollectionIsEmpty
ComputerList Then
ShowMessage No active
computers have logon older than [Var ThresholdDays] days.
Else
DoubleList Computers with
logon older than [Var ThresholdDays] days,Computer,Last Logon,[Collection ComputerList]
End If
Compiling the script
To compile your script into a single executable custom application, open the
script and go to the "Create Exe File" menu and select the "Save Script As Exe File"
menu item - or press F10.
Your script is now compiled into a single executable file. Remember to save a copy
of the script, as the executable file cannot be reverse engineered into the
original script. Please refer to
this page for more information on
pros and cons of custom applications versus executing the original script.
Summary
Watch Senior Technical Writer Steve Dodson from Binary Research International walk you through the
material presented on this page.